Over 3 million wheelchair users in the United States rely on proper securement systems every day. Knowing exactly how to secure a wheelchair prevents dangerous rolling, bouncing, or movement during transit—critical protection that could mean the difference between a routine trip and life-threatening injury in an accident. One moment of improper securement transforms a standard journey into a potential disaster.
This guide delivers the precise steps you need to master wheelchair securement without confusion. You’ll learn to identify proper attachment points, apply the four-point securement method correctly, and avoid the critical errors that compromise safety. By the end, you’ll confidently secure any wheelchair using professional techniques that keep you or your loved ones protected.
Choose Your Securement System Based on Needs

Manual Tie-Down Systems for Budget-Friendly Security
Manual tie-downs provide reliable wheelchair securement at the most affordable price point. These systems use four adjustable straps with metal J-hooks that connect your wheelchair frame to four floor anchor points. While requiring assistance from another person, they meet all safety standards when properly installed.
Key specifications to verify:
– Four straps with sturdy metal J-hooks
– Four floor anchor points (either loops or L-Track systems)
– Manual adjustment capability for each strap
– Confirmation that someone can assist with installation
Remember: You cannot drive from your wheelchair when using manual tie-downs. Always engage wheelchair brakes before beginning the securement process, and center your chair between anchor points facing forward for optimal safety.
Retractable Tie-Down Systems for Enhanced Convenience
Retractable systems solve the storage issues of manual tie-downs while maintaining security. Self-tightening mechanisms automatically remove slack, and quick-release buttons allow for faster disengagement. These systems work well for frequent travelers who need reliable security with reduced floor clutter.
Advantages over manual systems:
– Automatic retraction keeps straps organized when not in use
– Quick-release buttons enable faster disengagement
– Reduced floor space requirements
– Partial user operation possible with minimal assistance
While more expensive than manual systems, retractable tie-downs maintain the same fundamental four-point securement method. Always verify the straps are properly secured in the rail system before attaching to your wheelchair frame.
Wheelchair Docking Systems for Maximum Independence
Docking systems deliver unparalleled convenience for wheelchair drivers through electronic automatic securing. These systems require professional installation of a floor-mounted base and custom modification of your wheelchair with a locking bolt. The one-button operation makes securing and releasing effortless.
Essential features to consider:
– Electronic spring-loaded hook mechanisms
– Custom wheelchair modification with locking bolt
– Control module operation via easy-to-reach button
– Automatic engagement when properly aligned
– Backup mechanical release for electronic failures
Though the most expensive option, docking systems can replace any vehicle seat position and provide the highest security level. Never attempt DIY installation—professional setup is mandatory for safety and warranty compliance.
Prepare Your Securement Area Before Attaching Straps
Position Wheelchair Correctly for Optimal Security
Start by centering your wheelchair between anchor points while facing forward—never sideways. This positioning creates the proper strap angles needed for maximum stability. Check for adequate clearance from vehicle walls (minimum 6 inches) and ensure the floor area is free of debris before proceeding.
Critical positioning checklist:
– Wheelchair faces directly forward
– Centered between floor anchor points
– 6+ inches clearance from all walls
– Wheelchair brakes fully engaged
Power wheelchair users must also power down their chairs completely before securement begins. This prevents accidental movement during the attachment process that could compromise safety.
Identify Secure Attachment Points on Your Wheelchair
Your wheelchair’s attachment points determine security effectiveness. WC19-certified wheelchairs feature four clearly marked securement points designed specifically for vehicle transportation. For non-certified chairs, locate welded frame junctions or steel bolts with six raised lines on the bolt head.
Never attach straps to:
– Wheels or tires
– Armrests or footrests
– Removable components
– Adjustable parts or mechanisms
Tilt or recline wheelchair users must choose consistent attachment points—select either the seat frame or base frame for all four straps, never mixing between moving and stationary components.
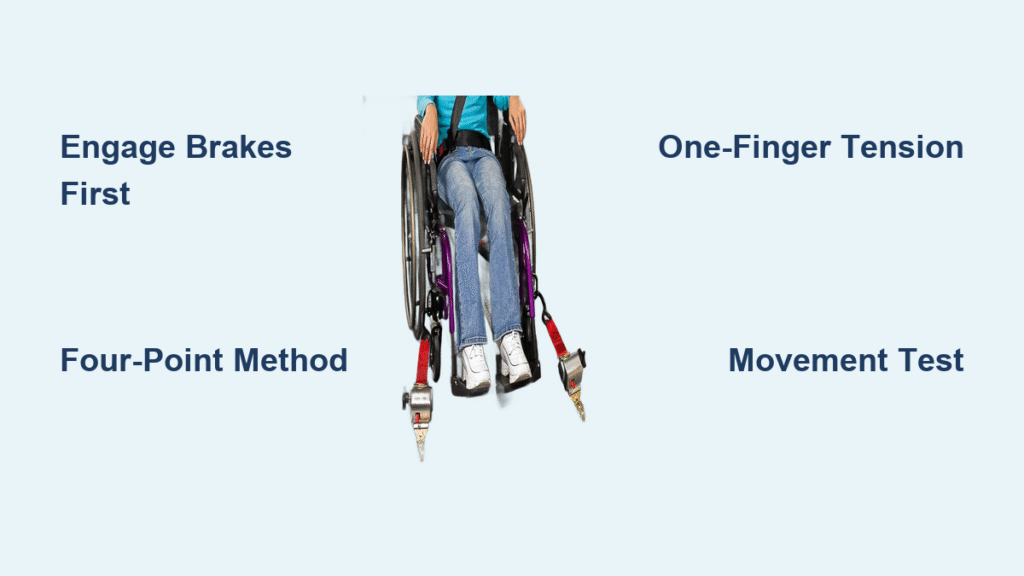
Master the Four-Point Securement Method Step-by-Step
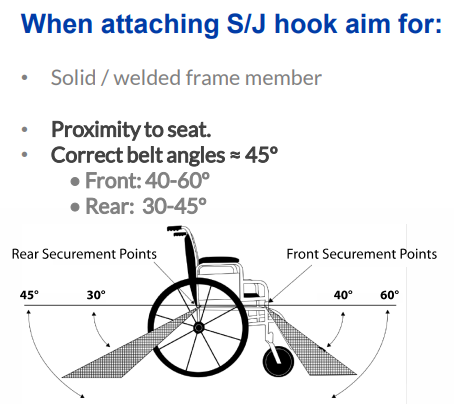
Attach Front Straps First with Proper Angle
Begin with the front straps, anchoring them wider than your wheelchair’s width. This creates a stable foundation that prevents forward movement during braking. Attach J-hooks to designated front frame points, ensuring they’re not twisted or caught on other components.
Front strap technique:
1. Hook to front frame junctions
2. Pull straps at 45-degree angle outward
3. Remove all slack before final tightening
4. Verify secure attachment points
Front straps should create a wider base than your wheelchair width for maximum stability. Test attachment by gently pushing the wheelchair forward—no movement should occur.
Secure Rear Straps with Correct Angle Configuration
Rear straps anchor directly behind your wheelchair, maintaining the critical 30-45 degree strap angle. This specific angle prevents both forward and rearward movement during sudden stops or turns while maintaining stability.
Rear strap configuration:
– Attach to rear frame junctions
– Maintain precise 30-45 degree strap angle
– Ensure equal tension with front straps
– Verify no wheelchair movement when tested
The rear strap angle is non-negotiable for proper security—angles outside this range compromise protection during accidents. Always check angles before finalizing tension.
Apply the One-Finger Tension Rule for Perfect Fit

Proper strap tension means you can fit exactly one finger under each tightened strap. Over-tightening damages wheelchair frames, while loose straps provide inadequate protection. Test tension by gently pushing your wheelchair from multiple angles after securing all four straps.
Tension verification steps:
– One finger fits comfortably under each strap
– No wheelchair movement when pushed firmly
– All four straps maintain equal tension
– Re-check tension after 5 minutes of driving
The one-finger rule prevents frame damage while ensuring adequate security. If you need to use more than one finger to fit under the strap, it’s too loose; if you can’t fit a finger at all, it’s dangerously over-tightened.
Complete Pre-Drive Safety Checklist Before Moving
Secure the Wheelchair User with Proper Restraints
Never rely solely on wheelchair securement straps for occupant protection. Lap belts must sit low across the pelvis, while shoulder belts cross the middle of the chest. Fasten restraints after securing the wheelchair but before starting the vehicle.
Occupant restraint protocol:
1. Fasten lap belt low across hips (not waist)
2. Position shoulder belt across chest center
3. Ensure belts aren’t twisted or pinched
4. Check for comfortable but secure fit
Both wheelchair and occupant must be secured independently—wheelchair securement systems protect against chair movement, while occupant restraints protect the person.
Perform the Critical Movement Test Before Driving
Conduct a comprehensive movement test before driving by pushing the wheelchair from front, back, and both sides. Any movement indicates improper securement requiring immediate adjustment.
Testing sequence to follow:
– Push forward firmly: Should not budge
– Push backward: Remains completely stationary
– Push left/right: Zero lateral movement
– Check brake engagement once more
If your wheelchair moves during testing, recheck all attachment points and strap tension. Never drive with a wheelchair that moves during this test—it indicates dangerous insecurement.
Avoid Critical Securement Mistakes That Compromise Safety
Never Skip Wheelchair Brake Engagement
Forgetting to engage wheelchair brakes remains the most common and dangerous mistake. Always engage brakes as your first step, before touching any straps. Electric wheelchair users must also power down their chairs completely to prevent accidental movement during securement.
Use Only Solid Frame Attachment Points
Weak attachment points fail catastrophically in accidents. Only solid, welded frame junctions provide the strength needed for crash protection. Look for WC19 certification marks or steel bolts with six raised lines to identify proper attachment points.
Frame point identification guide:
– Locate welded junctions on the frame
– Check for WC19 certification marks
– Avoid painted or coated surfaces
– Test attachment point strength before driving
Never attach straps to wheels, armrests, footrests, or any removable component—these will fail under crash forces.
Maintain Your Securement System for Long-Term Reliability
Conduct Daily Pre-Trip Inspections
Develop the habit of quick pre-trip inspections that take less than 60 seconds. Check straps for fraying, test anchor points for looseness, and verify all mechanisms operate smoothly. This simple routine prevents mid-trip failures that could compromise safety.
Daily inspection checklist:
– Strap condition (no fraying or cuts)
– Anchor point security
– Mechanism smooth operation
– Hook integrity and closure
Power wheelchair users should also verify battery connections and system power before each trip.
Mastering how to secure a wheelchair properly transforms from complex procedure to confident routine through consistent practice and attention to detail. Whether using basic manual straps or advanced docking systems, the four-point securement method remains your foundation for safety. Remember: proper securement isn’t just about following steps—it’s about building the muscle memory that makes safety automatic on every journey. Implement these techniques today to ensure you or your loved ones travel with maximum protection.